Stability and Determinacy of Structures
- Determinacy relates to the analysis of how fully a structure's internal forces and reactions can be determined using equations of equilibrium. A structure is considered determinate if all the internal forces and support reactions can be precisely calculated using static equilibrium equations.
- Stability refers to the ability to maintain equilibrium and resist failure or collapse. A stable structure is able to maintain equilibrium when subjected to external loads or forces, without undergoing excessive deformation or displacement. Statically Unstable occurs when the state of balance is disrupted, typically due to an inadequate number of supporting elements within a structure.
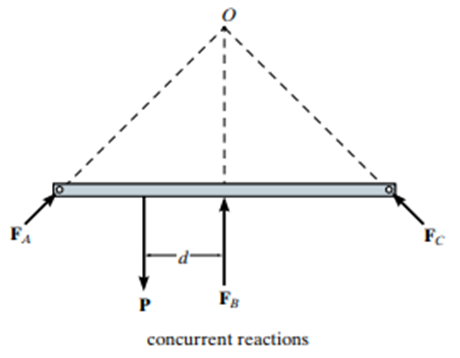
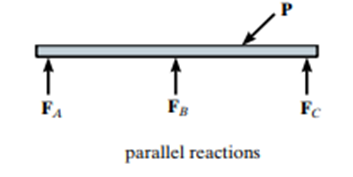
Formulations for Stability and Determinacy of Beams, Truss and Frames
| Structure Type | Condition | Stability / Determinacy |
|---|---|---|
| Beam | r < 3 + c | Beam is unstable |
| r = 3 + c | Beam is stable and determinate | |
| r > 3 + c | Beam is stable and indeterminate | |
| Truss | b + r < 2j | Truss is unstable |
| b + r = 2j | Truss is stable and determinate | |
| b + r > 2j | Truss is stable and indeterminate | |
| Frame | 3b + r < 3j + c | Frame is unstable |
| 3b + r = 3j + c | Frame is stable and determinate | |
| 3b + r > 3j + c | Frame is stable and indeterminate |
Where:
r = Total number of reactions
c = Equations of condition (c = 1 for a hinge; c = 2 for a roller; c = 0 for a beam with internal pin connection)
b = Number of members
j = Number of joints
Beam Stability and Determinacy Examples |
|||
|---|---|---|---|

|
|||
| Given | Computation | Condition | Result |
| R = 5, m = 1 | 5 > 3(1) | r > 3 + c | Indeterminate |
| R = 5, C = 0 | 5 > 3 + 0 | r > 3 + c | Beam is stable and indeterminate |

|
|||
| Given | Computation | Condition | Result |
| R = 7, m = 2 | 7 > 3(2) | r > 3 + c | Indeterminate |
| R = 5, C = 1 | 5 > 3 + 1 | r > 3 + c | Beam is stable and indeterminate |

|
|||
| Given | Computation | Condition | Result |
| R = 6, m = 2 | 6 = 3(2) | r = 3 + c | Determinate |
| R = 4, C = 1 | 4 = 3 + 1 | r = 3 + c | Stable and determinate |

|
|||
| Given | Computation | Condition | Result |
| R = 11, m = 4 | 11 < 3(4) | r < 3 + c | Unstable |
| R = 7, C = 2 | 7 > 3 + 2 | r > 3 + c | Unstable internally |
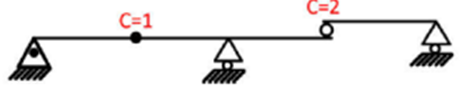
|
|||
| Given | Computation | Condition | Result |
| R = 7, m = 4 | 7 < 3(4) | r < 3 + c | Unstable |
| R = 4, c = 3 | 4 < 6 | r < 3 + c | Unstable |