Distribution of Floor Loads (One way and Two Way Slabs)
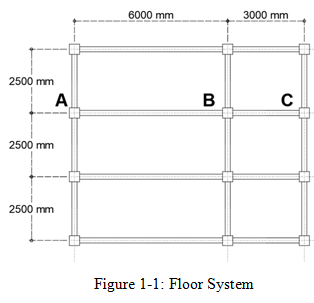
This is an example of how to compute and distribute loads to beams from one-way or two-way slabs. In Figure 1-1, if the ratio of the short spans to the long span is greater than \(2(\frac{L}{S}>2)\), the floor is a one-way slab and a Two-way slab if the opposite\((\frac{L}{S}\le 2)\).
Example
Given a live load of 2.9 kPa, draw the live load to be applied on the beam AB and BC. Assume a simply supported beam on AB and on BC.
Span AB: \(\frac{L}{S}= \frac{6}{2.5}=2.4 > 2.0\)
Thus, the slab along beam AB will be one-way slab
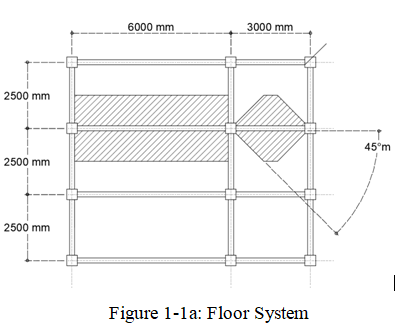
Span BC: \(\frac{L}{S}= \frac{3000}{2500}=1.2 < 2.0 \), the slab along beam BC is a two-way slab.
Load Distribution along Beam AB will be distributed as a uniformly distributed load.\(WL= \frac{2.5}{2} (2.9)(2)=14.5 kN/m \)
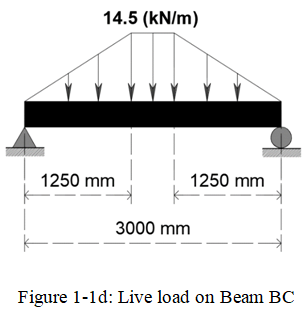
Load Distribution along Beam BC, will be distributed as a trapezoidal load\(WL= \frac{2.5}{2} (2.9)(2)=14.5kN/m \)
Solve for the dimension of the trapezoid, refer to figure 1-1b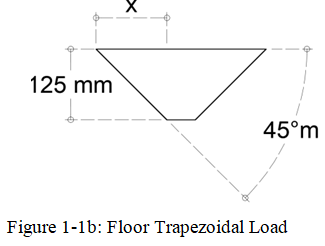
\(\tan{45} = \frac{x}{125}\)
\(x = 125\) mm
Apply the Live load on the Beam AB, refer to Figure 1-1c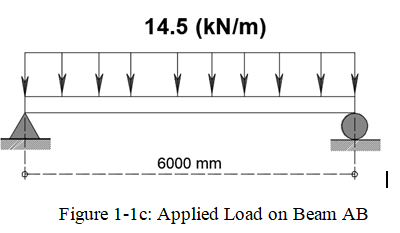 Apply the Live Load on Beam BC (See Figure 1-1d)
Apply the Live Load on Beam BC (See Figure 1-1d)